 Evolution & Systematics Evolution & Systematics 
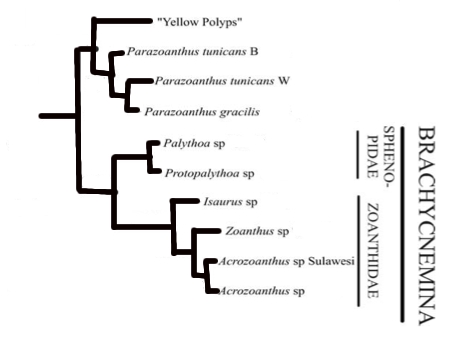
(Fig 1. Phylogenetic tree of the mitochondrial sequences from Sinniger et.al. 2005)
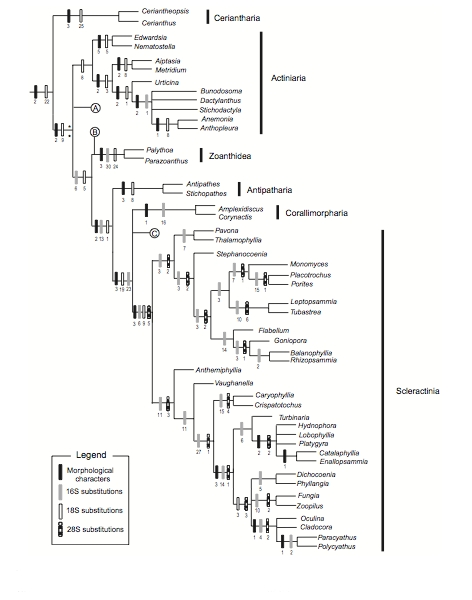
(Fig 2. Phylogenetic tree constructed by Daly et.al. 2003)
Molecular sequences and morphological characteristics are used to determine the evolution of organisms. Previous phylogeny studies were conducted to examine the phylogeny relationship between Anthozoa. Based on the arrangement of the septa, the Zoanththaria can be divided into 2 suborder, Macrocnemina and Brachycnemina (Spinniger et.al 2005). Within the Brachycnemina, Palythoa and Protopalythoa can closely related. Based on the result from Daly et.al.2003; Burnett et.al. 1997 and Spinniger et.al 2005, the picture above show the evolutionary link among these species. Morphological characteristics such as the number of tentacles and septa, colour, the shape and position of sphincter muscle and the size and distribution of different nematocysts are the key characteristics to discriminate species (Spinniger et.al 2005). In recent study, their result indicated that there were no clear phylogenetic distinction can be may between P.tuberculosa and P.caesia, however they have shown that P.tuberculosa and P.caesia are phylogenetically more related than P.tuberculosa and P.mutuki (Hibino et.al. 2013).

(Fig 3a & b. (a)Maximum likelihood trees of mitochondrial 16s rDNA sequences, (b) mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase subunit 1 sequences, both tree constructed by Hibino et.al. 2013)

(Fig 4. Maximum likelihood trees of nuclear ITS-rDNA sequences constructed by Hibino et.al. 2013)
|