~ ~ ~
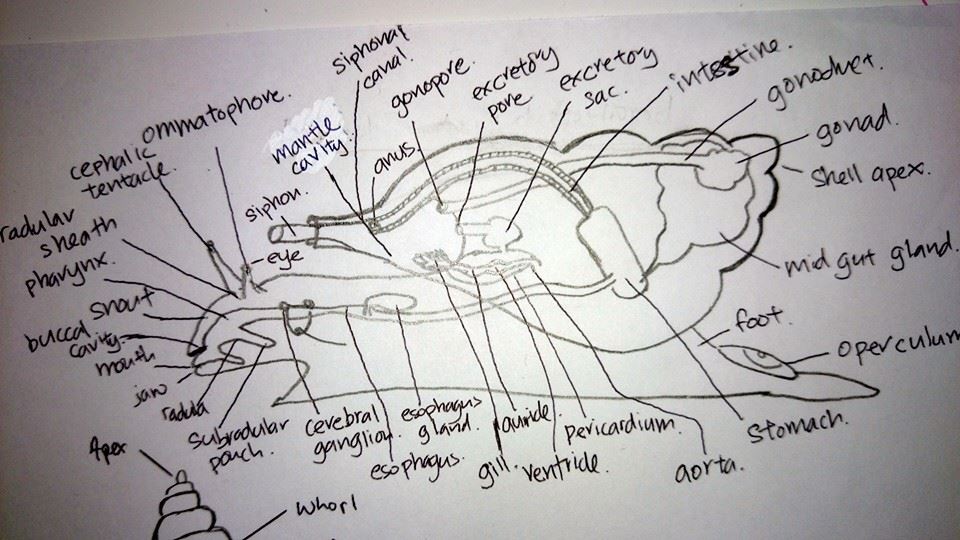
Internal anatomy of Turbo undulatus, adapted from Richard, C. B. and Gary, J. B. (2003) Invertebrates California: Sinauer Associates
Ommatophore A structure on the head, one of two tentacle-like projections bearing eyes; may be seperate structure or more or less fused with cephalic tentacles.
cephalic tentacle Pair of large tentacles on head; may be associated with ommatophores and thus closely adjoin or be fused with eye, or may be modified into cephalic shield. Innervated by cerebral ganglion. (smooth, fringed)
radula shealth Elongate sheath producing and eclosing radula and radular membrane. Term radular sac may refer only to posterior, somewhat expanded section of radular sheath. (short, elongate, looped, coiled, posteriorly bifurcated, V-shaped)
Pharynx Muscular section of digestive tract between buscal cavity and esophagus. Received various glands and is associated with radular apparatus.
snout anterior noninvaginable extension of head bearing terminal mouth; may be drawn out into pair of labial palps.
buccal cavity Somewhat expanded, cuticle-lined section of digestive tract between mouth and pharynx; typically bears pair of jaws laterally.
mouth Anterior opening of digestive tract; may be positioned on prolongation of head (snout, proboscis) and be surrounded by various labial projections. Opens into buccal cavity. (circular, slit-like, T-shaped)
jaw Pair of separate or fused cuticular elements in lateral wall of buccal cavity; movable by special muscles. Considered to form border between buccal cavity and pharynx.
radula Specialized, protrusile armature of anterior region of digestive tract. Refers to full complement of chitinized teeth along radular membrane. (doccoglossate, hystrichoglossate, ptenoglossate, rachiglossate, rhipidoglossate, taenioglossate, toxoglossate)
subradular pouch In digestive tract, flat sac extending posteriorly below radula; roof of subradular pouch may include subradular organ.
cerebral ganglion One of two concentrations of nerve tissue located above anterior section of digestive tract and representing nervous centre, connected dorsally to each other by cerebral commissure, occasionally also ventrallyby subcerebral commissure. Gives rise to nerves innervating head region and associated sense organs; may more closely adjoin additional ganglion to form circumenteric nerve ring.
esophagus Elongate section of digestive tract between pharynx and stomach; may bear esophagael pouch, esophagael bulb, crop, or gland of Leiblein, and is characterized internally by longitudinal folds.
esophageal gland Pair of glandular pouches opening into lateral part of beginning of esophagus. May be modified into gland of Leiblein.
auricle Relatively thin-walled chamber of heart receiving blood from ctenidium or respiratory surface and pumping it via ventricle into aorta. Reduction of one ctenidium generally leads to loss of one auricle. (single, paired)
gill Respiratory organ, primitively a ctenidium yet including other outgrowths and respiratory appendages.
siphon Anteriorly directed, trough-like or tubular extension of mantle margin; typically partially enclosed in siphonal canal of shell. Serves to direct water into pulmonary sac or mantle cavity.
amntle cavity
anus Posterior opening of digestive tract; opens in mantle cavity or at its vestigial area, in typical (torted) snail anteriorly along with gonopore and excretory pore.
gonophore Opening of male or female reproductive system to exterior; typically located in mantle cavity where it forms part of pallial complex.
excretory pore Ciliated, muscular opening of excretory system to exterior; typically located in mantle cavity, forming part of pallial complex, yet also opening onto body surface or into rectum. (single, paired)
excretory sac Expanded, often regionated and internally folded section of excretory system; connected to pericardium via renopericardial canal, to excretory pore via excretory canal (ureter). (simple, lobulated, branched)
intestine Section of digestive tract between stomach and rectuml in typical (torted) snail, intestine proceeds anteriorly along or through pericardium in direction of mantle cavity. (straight, coiled, looped)
gonoduct Hermaphroditic duct, oviduct, sperm duct, spermoviduct.
gonad Ovary, ovotestis, testis.
midgut gland Large, typically unpaired digestive gland opening into stomach via duct(s); may form greater part of visceral mass. (single, paired)
foot Part of body, typically in the form of a muscular creeping sole separated to varying degrees from head and visceral mass and which may be retracted into shell. May be regionated and bear operculum on posterior end.
operculum Lid like structure serving to close aperture when snail retracts into shell; borne on posterior end of foot and composed of organic material (similar to periostracum) strengthened to varying degrees by calcareous material.
stomach Weakly muscularized section of digestive tract between esophagus and intestine; recieves midgut gland. Located at the point in which digestive tract
aorta Major blood vessel leading from ventricle of heart; typically divides into anterior and posterior aortas supplying the major organs.
pericardium Fluid-filled chamber enclosing heart and connected to excretory system via renopericardial canal.
ventricle Muscular chamber of heart receiving blood from auricle(s) and pumping it into aorta; typically separated from auricle by auriculoventricular valve
The above information was retrieved from Stachowitsch, M., 1992. The invertebrates An Illustrated GlossaryNew York, New York : Wiley-Liss
|