Anatomy & Physiology
Tunic
The ascidians have their bodies surrounded by an exoskeleton called a tunic. This tunic, composed of proteins, carbohydrates and tunicin fibers is unique to ascidians. One of the main features of the Phallusia julinea’s tunic is the bright yellow chromatophores it contains, which gives its color to the ascidian. Chromatophores are pigmented light-reflecting organelles found in some cells located inside the tunic.
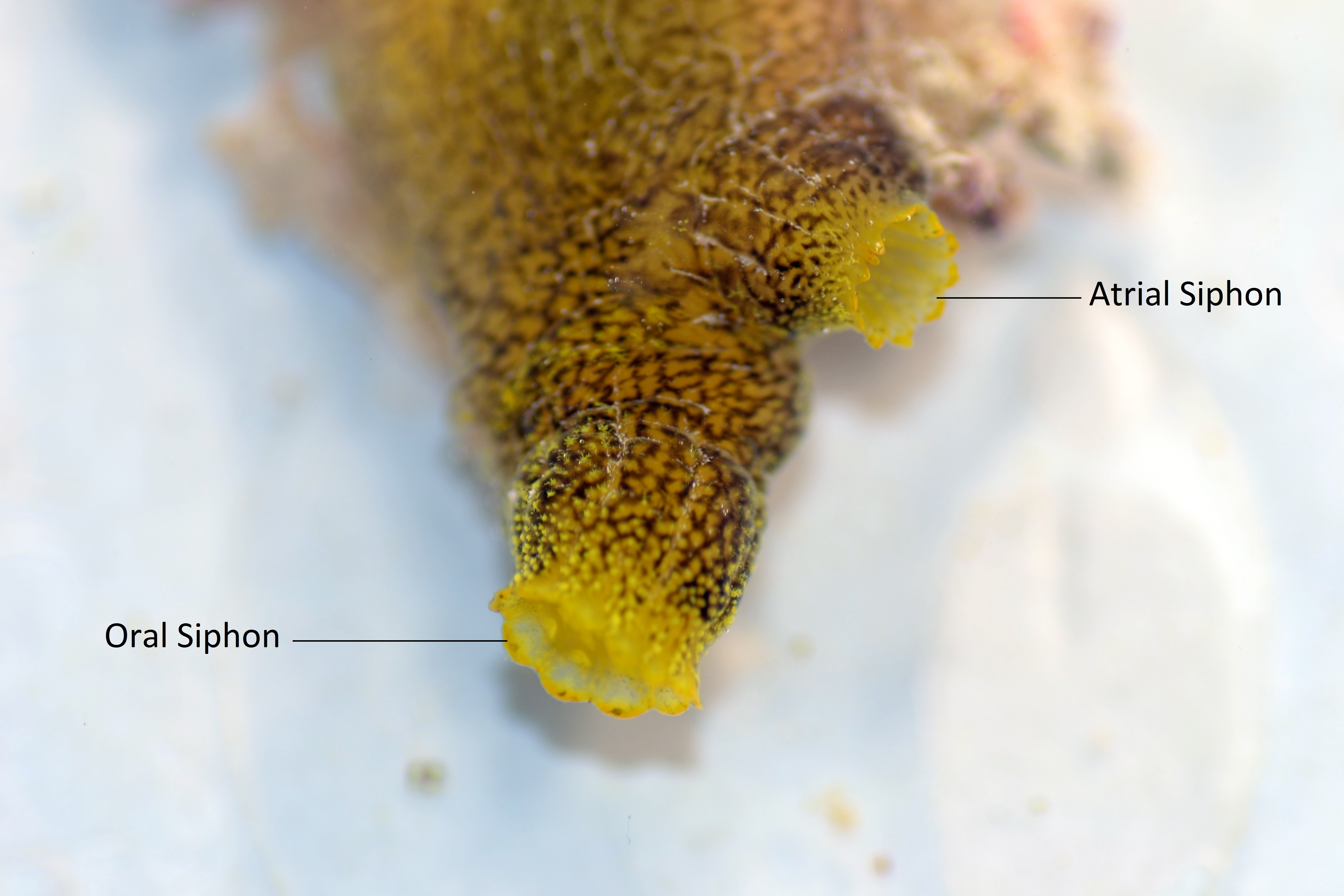
The tunic is not tightly fixed to the body of the ascidian, except around the siphons, and is also used by the animal to be fixed on the ground.
Siphons
Ascidians have two main siphons, the oral (or Branchial) and atrial siphons. The oral siphon is situated on the posterior end of the Phallusia julinea and is the inhalant siphon,while the atrial siphon is located on the dorsal side of the animal and it exhales the water. Both are indented.

Pharynx
Ascidians have a pharynx that covers the whole length of their thorax where the branchial basket is located. The water coming from the oral siphon goes by the thorax, through the branchial basket, before leavingthe ascidian body via the atrial siphon. The branchial basket is responsible for creating the water current (Peterson 2007).
The ventral side of the thorax is covered by the endostyle which is a deep groove lined with ciliated glandular epithelium secreting the mucus net (Australian Museum 1985).
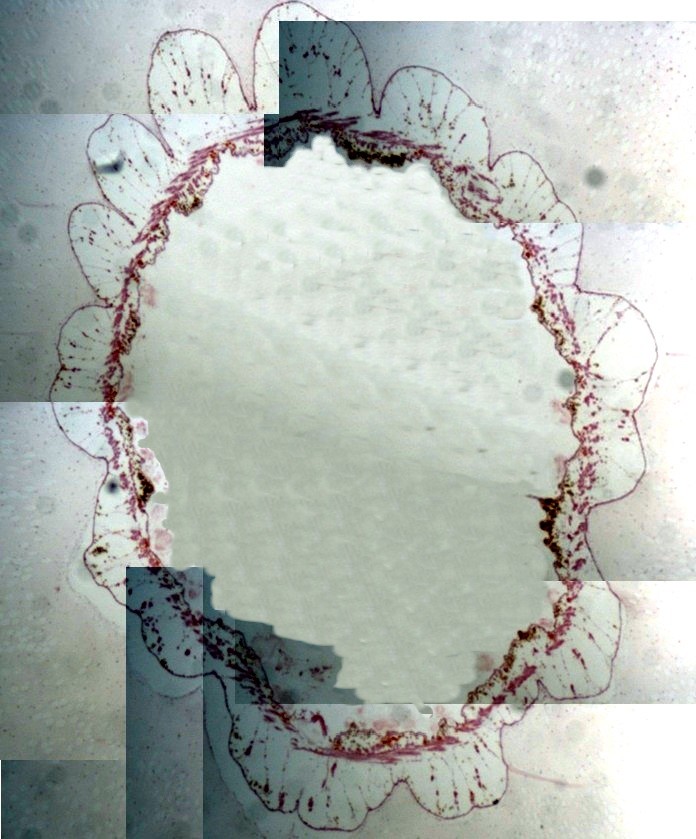

Reconstituted histology of the Phallusia julinea branchial basket.
Digestive system
The branchial basket is linked to a stomach, where the food caught in the mucus net is sent to. The anus is located on the dorsal side of the animal, to excrete waste directly in the atrium. This position is possible because the midgut and hindgut make a loop in the body.
Haemal system
The heart is located between the pole of the gut loop and the pyloric region. There is a large quantity of red blood cells. The blood is usually carried through vessels, especially around the branchial sac, but it is not uncommon to find blood cells in the tunic.
Immune system
Aggregations of immune cells, also called morula cells, were found after looking at the prepared histology of Phallusia julinea.
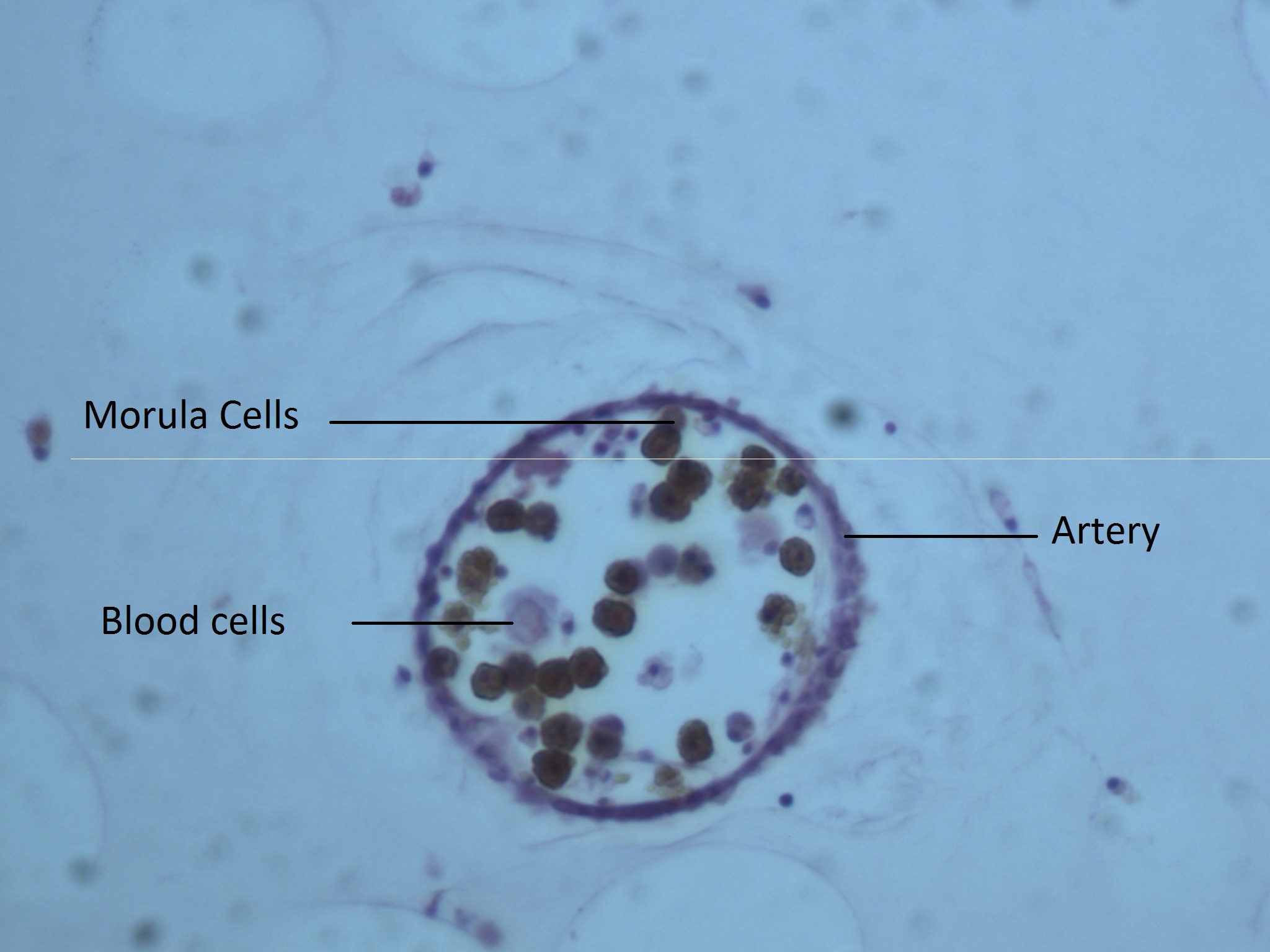
Morula cells present in an artery going through the tunic.
Reproductive organs
Ascidians are hermaphrodites; they produce both eggs and sperm. Both the ovaries and sperm duct are situated close to each other in the thorax of the animal.
The ovaries are usually tubular or sac-like while the sperm duct is often coiled around it.
Nervous system
Contrary to other chordates, ascidians do not have a brain, but a neural ganglion, often positioned behind the atrial siphon.
Larvae
The ascidian larvae are similar to any other chordate larvae, but they lose most of the organs during metamorphosis.
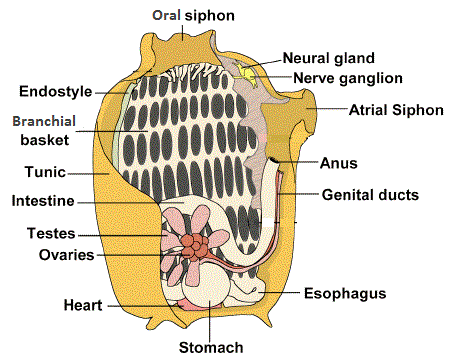
Figure 1. Anatomy of an ascidian, adapted from http://www.sms.si.edu/irlfieldguide/AscidianBiol.htm.
Sources for the whole section: Kott 1985, Brien et al. 1948 and Ruppert et al. 2004.
Did you know?Ascidians are the only animals that can actually reverse thedirection of blood flow in their circulatory system. |