Defense Mechanisms
Holothuria impatiens defends itself by shooting cuvierian tubules out of its anus onto a predator (Ruppert, et al 2004). These tubules are usually discharged 2 at a time and are incredibly sticky. This is quite an effective method to use when moving quickly is not an option. The cuvierian tubules are essentially enlargements of the respiratory tree that lie within the coelom of the sea cucumber (Kerr 2003). Depending on the species, replacement tubules can grow back between 7 days and 5 weeks (Kotpal, 2009). As of yet there is no information on the rate at which H. impatiens re grows its tubules.
In some species of sea cucumber, the cuvierian tubules are laced with a toxic chemical known as holothurin, however, in 1974 Bakus found that in H. impatiens, the toxin is located within the body wall. This chemical is another effective way that sea cucumbers are able to defend themselves (Kotpal, 2009).
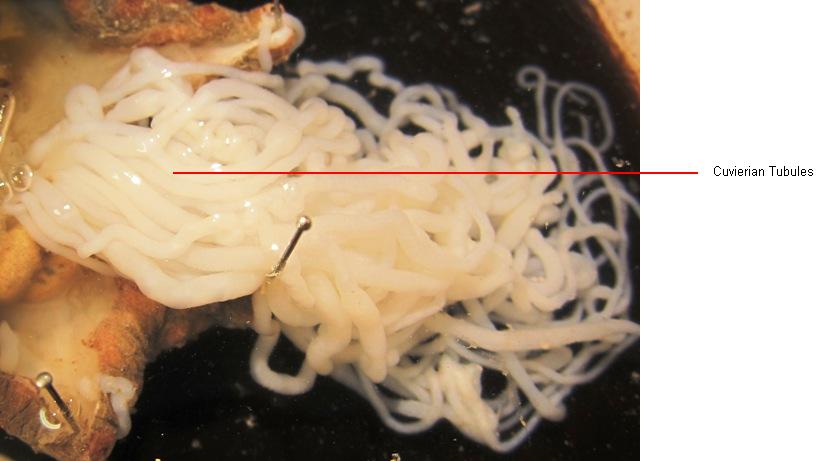
Figure 5: Cuvierian tubules extracted from a dissection of the Holothuria impatiens.
|